Bridge Curves
When you take off elements from a laser or CNC machine after cutting process ,sometime you want the items to remain connected together rather than mixing them up and spend time on sorting later on. If that is what you struggle with in your workshop, then we have Bridge Curve plug-in for you! The plug-in connects the element together by making small bridge between each pair. The elements remain connected till you break those tiny connections.
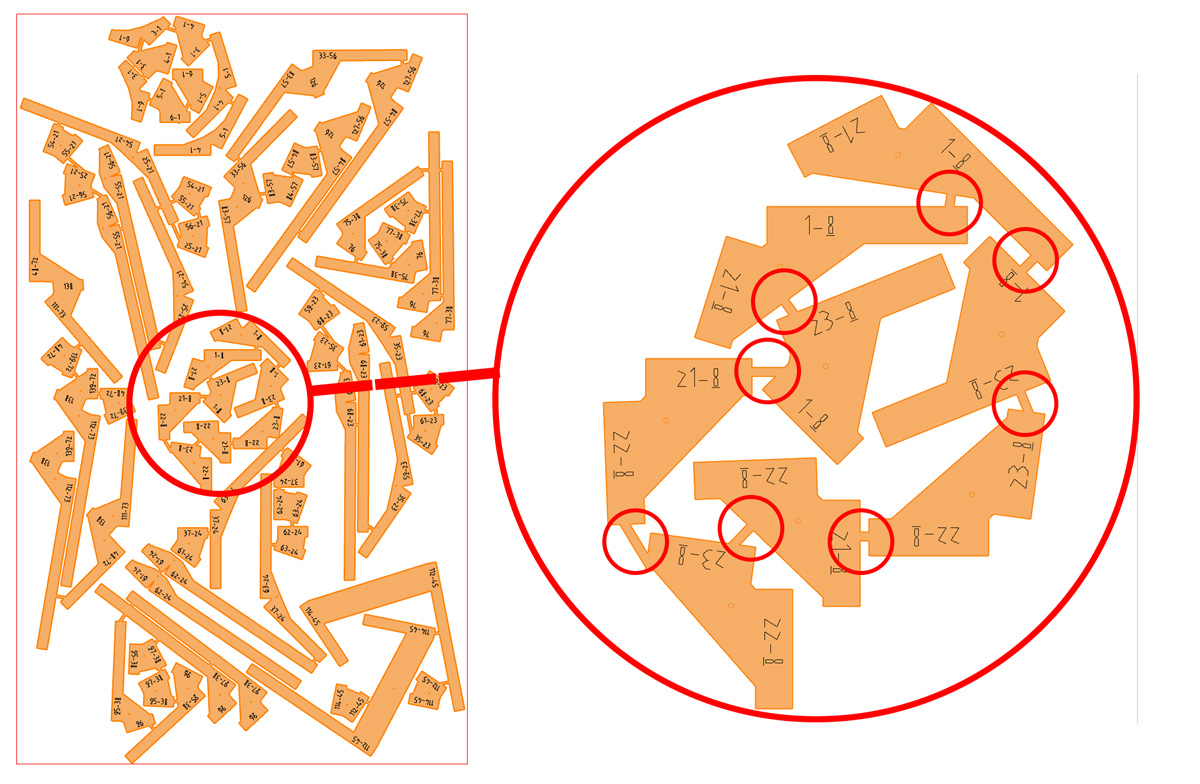
Shortest path problem
The program uses an evolutionary algorithm to find the best possible sequence of the curves in which by connecting them the shortest path is achieved. In the other words the total length of the bridges are always minimized. In order to keep the corners intact, the algorithm uses a safe distance and makes sure the bridges are not built exactly at the corners. This helps to prevent undesired results after breaking the connections.
Download
The plugin is available for Rhino 6 and Rhino 7, please read the instruction inside the package for the installation.
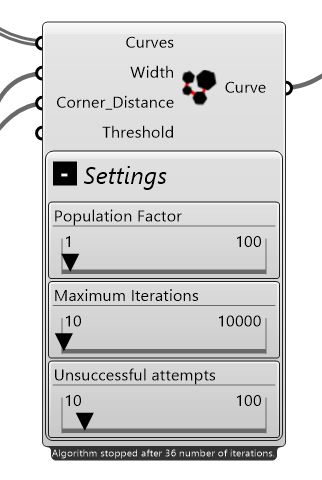
Curves
The set of curves to be connected together. The curves must be closed otherwise undesired results may occur.
Width
Controls the width of the bridge. While setting this parameter pay attention to the thickness of the material and the size of the elements.
Corner Distance
If it happens that the connection is made at a corner of the a curve, the connection will then be offset using this amount to avoid the corner.
Threshold
Two curves are connected together only if the minimum distance between them is less than this threshold.
Unsuccessful attempts
The algorithm stops after this many consecutive unsuccessful attempts. An unsuccessful attempt is an iteration of the evolutionary algorithm which do not increase the quality of the best chromosome.
Maximum Iterations
Defines the maximum number of iterations that genetic algorithm will run. Increase this value if you are not satisfied with the result.
Population factor
Controls the size of population for the evolutionary algorithm. The actual number of population is defined by multiplication of this factor and number of curves. Higher values produce better results in more time.